Doing microservices with JHipster
Microservices vs Monolithic architecture
The first question JHipster will ask you is the kind of application you want to generate. You have the choice between two architecture styles:
- A “monolithic” architecture uses a single, one-size-fits-all application, which contains both the front-end Angular code, and the back-end Spring Boot code.
- A “microservices” architecture splits the front-end and the back-end, so that it’s easier for your application to scale and survive infrastructure issues.
A “monolithic” application is much easier to work on, so if you don’t have any specific requirements, this is the option we recommend, and our default option.
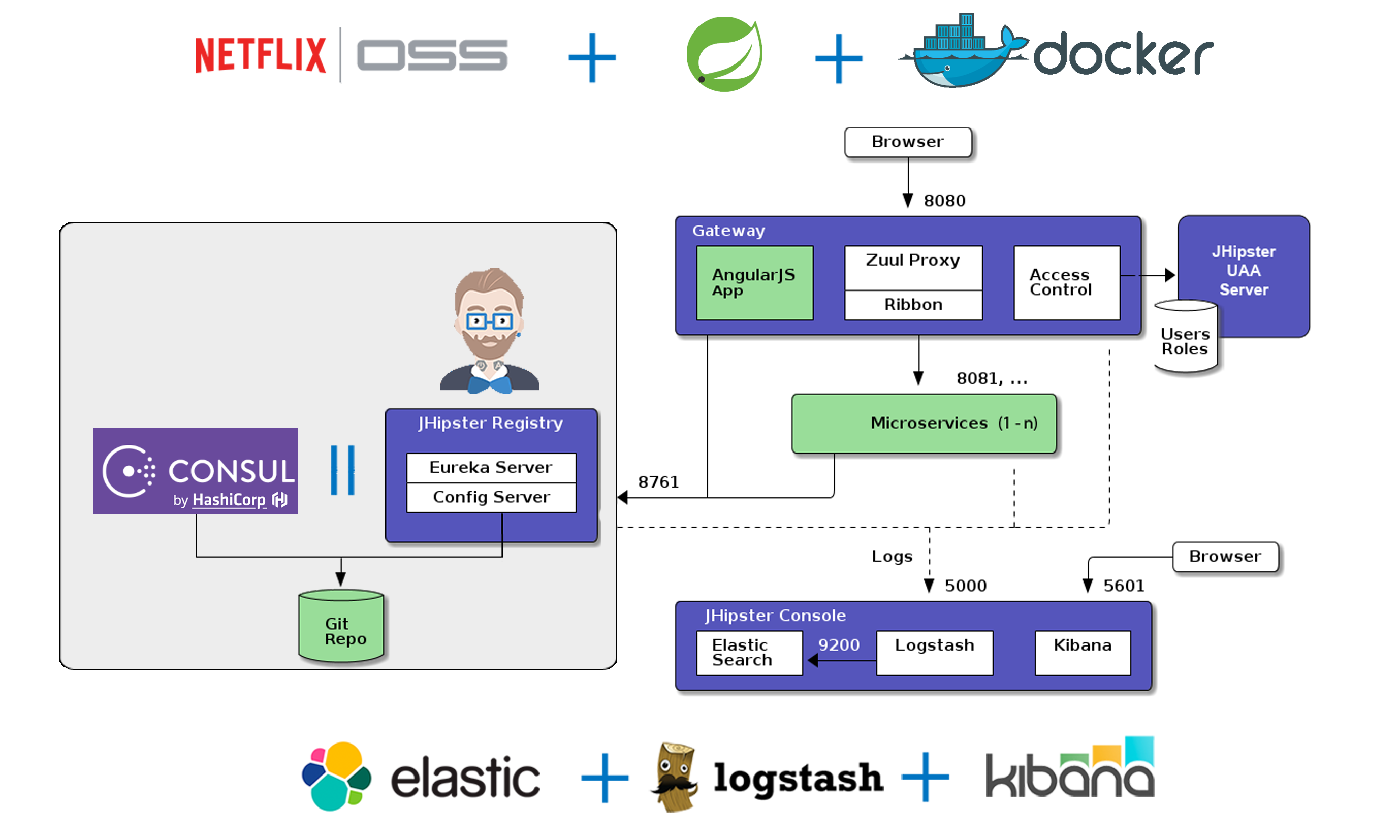
Microservices architecture overview
The JHipster microservices architecture works in the following way:
- A gateway is a JHipster-generated application (using application type
microservice gatewaywhen you generate it) that handles Web traffic, and serves an Angular application. There can be several different gateways, if you want to follow the Backends for Frontends pattern, but that’s not mandatory. - The JHipster Registry is a runtime application on which all applications registers and get their configuration from. It also provides runtime monitoring dashboards.
- Microservices are JHipster-generated applications (using application type
microservice applicationwhen you generate them), that handle REST requests. They are stateless, and several instances of them can be launched in parallel to handle heavy loads. - The JHipster Console is a monitoring & alerting console, based on the ELK stack.
In the diagram below, the green components are specific to your application and the blue components provide its underlying infrastructure.